Veterinary Diagnostic Lab in Rochester
We have advanced tools at Ridgemont Animal Hospital to help diagnose your pet's medical issues. We provide a wide range of services, including digital radiology, EKG, and blood tests.
We use radiographic imaging that allows us to produce highly detailed images of your pet's internal structures.
With our diagnostic imaging capabilities, we can efficiently produce diagnostic information about your pet's condition and provide immediate treatment options.
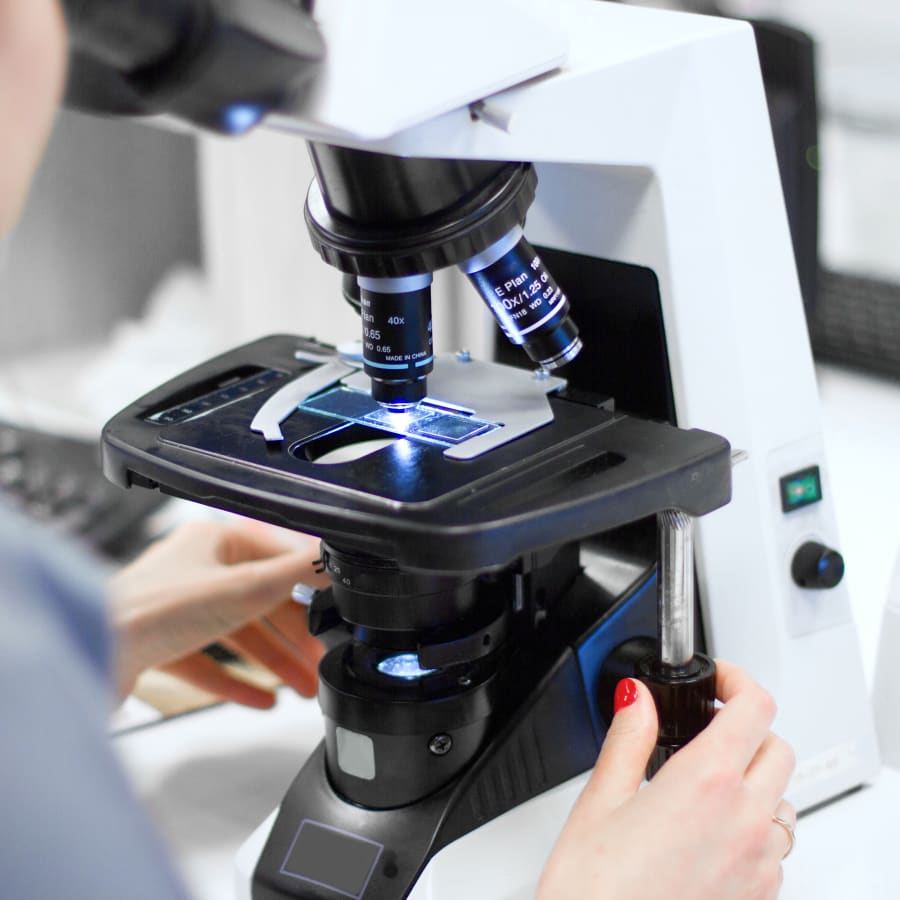
In-House Lab & Vet Pharmacy in Rochester
We perform tests and get results quickly in our veterinary diagnostic laboratory so that we can diagnose your pet's symptoms and begin treatment as soon as possible.
Our Rochester pet pharmacy is stocked with a variety of prescription diets and medications, allowing us quick access to any medications your pet may require while in our care.

Veterinary Diagnostic Services at Ridgemont Animal Hospital
With our in-house vet lab, we are pleased to offer advanced diagnostic testing to allow our vets to provide rapid diagnosis of your pet's medical issues.
-
Radiography (Digital X-rays)
Using a radiograph (digital x-ray), we can examine your pet's internal systems to reveal information that may be invisible from the outside.
Radiography is a non-invasive, painless procedure. It only employs very low doses of radiation. Because the level of radiation exposure required for radiography is so low, even pregnant pets and very young pets can have this procedure performed.
Radiographs can be used to evaluate bones and organs, and diagnose conditions including broken bones, chronic arthritis, bladder stones, spinal cord diseases, and some tumors.
-
Bloodwork
At our vet lab in Rochester, we are able to run a number of common and specialized blood tests to determine the health of your pet, and to diagnose illness.
CBC (complete blood count), white blood count, hemoglobin and MCHC (mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration), hematocrit, platelets, eosinophils, and blood serum profile are some of the most common veterinary blood tests we perform.
-
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is a key diagnostic test that provides your vet with essential insights into the physical and chemical properties of your pet's urine.
Urinalysis is primarily used to evaluate the health of your animal's kidneys and urinary tract system, but it can also be useful in detecting problems in other organ systems and is critical in diagnosing metabolic diseases such as diabetes.
This is a valuable diagnostic test for both healthy and sick animals and should be included in any comprehensive evaluation of your pet's overall health.
-
Fecal Exam
A fecal exam is the microscopic examination of your pet's feces, which can be done at our in-house vet lab in Rochester.
The ultimate goal of a fecal exam is to identify and treat any GI infections that may be threatening your pet's or your family's health. Fecals enable your veterinarian to determine whether your pet has intestinal parasites like roundworms or hookworms.
Parasites can make pets uncomfortable, and irritable, and lead to more serious conditions. Some can even be transmitted to humans.
Since these parasites live in your pet’s gastrointestinal tract, they are often hidden from view. The only way to detect them is with a fecal exam.
Annual fecal examinations should be a vital part of every pet's routine wellness exam.
-
ECG/EKG
If your veterinarian performs a physical examination and suspects your pet may have a heart disorder, we usually take chest X-Rays and an electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG).
This procedure is simple and quick to complete. It reveals information that may be critical to your pet's diagnosis. In other cases, a cardiac ultrasound may be required to identify problems in the heart's chambers.
-
Veterinary Blood Pressure Monitor
With our veterinary blood pressure monitor, we can take animal-specific and accurate measurements of your pet's blood pressure, both awake and sedated, during your pet's routine exam or surgery.
When a pet has high blood pressure, it means that his or her blood vessels have become too narrow to handle the increased blood pressure flow. It is important to diagnose high blood pressure in pets, or they may begin to suffer organ damage (with the eye being particularly vulnerable).
New Patients Welcome
Ridgemont Animal Hospital is accepting new patients! Our experienced vets are passionate about the health of Rochester companion animals. Get in touch today to book your pet's first appointment.
Contact
Hours
-
Click to View
- Monday:08:30 am - 06:00 pm
- Tuesday:08:30 am - 06:00 pm
- Wednesday:08:30 am - 06:00 pm
- Thursday:08:30 am - 06:00 pm
- Friday:08:30 am - 05:30 pm
- Saturday:Closed
- Sunday:Closed
